“The city of birth will be as much a unique part of your life as your descent from your mother.”
Albert Einstein, 1929
ALBERT EINSTEIN IN ULM, 1879 – 1880
Hermann Einstein (1847-1902), born in Buchau on the Federsee and merchant in Ulm, married 18 year-old Pauline Koch (1858-1920) from Cannstatt, the daughter of a purveyor to the royal household and corn-merchant in Stuttgart, on August 8, 1876. At first Hermann Einstein and his young wife lived at the “Suedlicher Muensterplatz” in Ulm. He was the joint owner of a company trading with feather-beddings at Weinhof A 90 (“Zum Engländer”, later renamed to Weinhof 19). Ulm was then a soaring town of some 33000 inhabitants with two percent among them being Jews. The Einsteins, also being of Jewish ancestry, participated in the religious life of the Jewish community. In 1878/79 Hermann Einstein and his pregnant wife moved to a new and larger residence at Bahnhofstrasse B 135 (in 1880 renamed to Bahnhofstrasse 20) in Ulm.
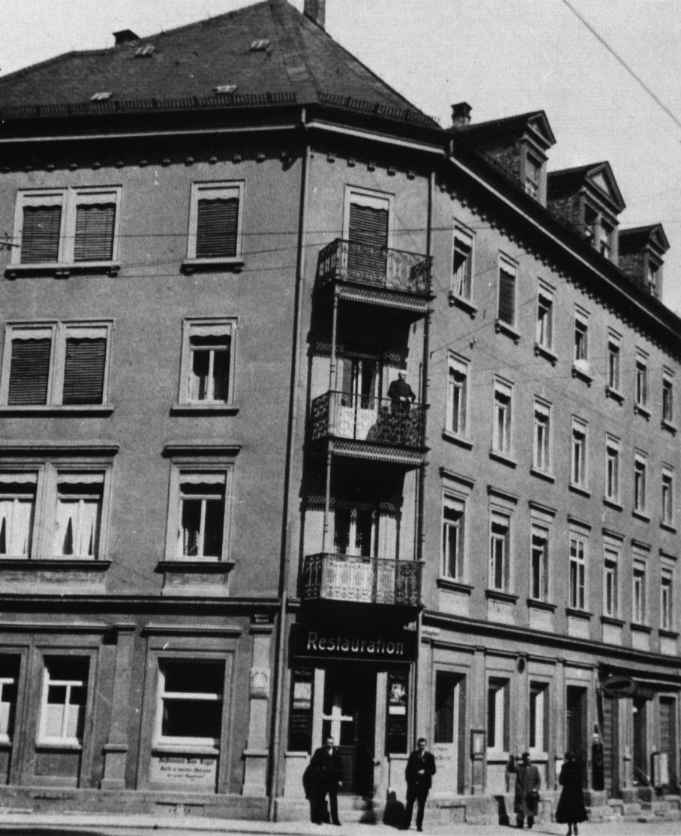

Einstein’s birth-place
About his birth-place in the Bahnhofstrasse 20, in a letter to Carlos Erlanger, son of the house-owner at that time, Einstein wrote in April 1929: “To be born the house is quite nice because on this occasion one does not yet have major aesthetic needs; instead one cries at his beloved ones without worrying much about reasons and conditions.”
The house, erected in 1871, was destroyed in December 1944 during one of the heaviest bombardments of Ulm. Einstein did not have any special relation to his birth-place. When he was shown a photo of his destroyed birth-place he wrote in his reply: “Time has affected it even much more than it has affected me.”
On March 14, 1879, a Friday, Pauline Einstein gave birth to her first child, a boy, in their residence in the Bahnhofstrasse. On the following day Hermann Einstein registered his son at the registry office in Ulm with the name Albert.
As the back of the head seemed much too big, the family initially considered a monstrosity. The physician, however, was able to calm them down and some weeks later the shape of the head was normal. When Albert’s grandmother saw him for the first time she is reported to have muttered continuously “Much too fat, much too fat!” Contrasting all apprehensions Albert grew and developed normally except that he seemed a bit slow.
Financially Hermann Einstein and his family were able to live a more or less untroubled life in Ulm. However, at the initiative of his younger brother Jakob, Hermann Einstein moved with his wife and the one year old Albert to Munich during the summer of 1880. There Hermann Einstein had the opportunity to become partner of his brother’s company Einstein & Cie. On June 21, 1880 Hermann Einstein registered himself and his family with the police. Thus after only 15 months Albert Einstein’s stay in Ulm had come to an end.
Until the present day it is not entirely clear whether Einstein ever visited his birth-place again. From several surviving letters, however, there is evidence that he might have visited Ulm briefly on passing through.
Ulm and Einstein
In 1920, after Einstein’s achievements had been widely recognized, Ulm also wanted to honour him. Thus, for example, in 1922 the decision was made to name a yet to be constructed street after him. Even though in Nazi-Germany this street was renamed Fichtestrasse (after Johann Gottlieb Fichte, 1762-1814, a German philosopher), it was named Einsteinstrasse again in 1945. On the occasion of his 50th birthday on March 14, 1929, Einstein was informed in a letter of congratulation by the then mayor that the city of Ulm had named a street in his honour. With respect to the Einsteinstrasse Einstein remarked in his reply: “I have already heard about the street named after me. My comforting thought was that I am not responsible for whatever is going to happen there.” Between 1920 and 1929 a lively exchange of notes between Ulm and Albert Einstein developed which, interrupted by the political situation in Germany, was only resumed in 1949.
In 1949 Ulm wanted to grant Einstein the rights of a freeman of the city. Einstein however declined, pointing to the fate of the Jews in Nazi-Germany.
While Einstein was still alive and also after his death in April 1955 several ceremonies and commemoration days were held in his honour.
At present, apart from the above-mentioned Einsteinstrasse, in Ulm you can find a memorial and a memorial tablet in the Bahnhofstrasse. In addition, the building of the “Volkshochschule” (school for adult education) carries the name “EinsteinHaus”. When laying the foundation-stone to the “EinsteinHaus – Haus der Volkshochschule” in January 1966 the nobel laureates Max Born (1882-1970), Otto Hahn (1879-1968) and Werner Heisenberg (1901-1976) were present. Since 1968 there is a permanent photographic exhibition in the first floor of the EinsteinHaus where the life of Albert Einstein is re-traced in a selection of individual photographs, arranged by Professor Hans (Nick) Roericht. Information about this exhibition is available under info@vh-ulm.de.
On the occasion of the 125th birthday of Albert Einstein a ceremonial act took place in the Congress Centre in Ulm on Sunday, March 14, 2004. After the lord mayor Ivo Gönner welcomed the audience, Johannes Rau, the prime minister of Baden-Württemberg Erwin Teufel and the head of the “Deutsche Physikalische Gesellschaft” (German Physical Society), professor Roland Sauerbrey held a speech. The ceremonial speech was held by doctor Albrecht Fölsing. The ceremonial act was musically accompanied by the Philharmonic Orchestra of the city of Ulm under the direction of James Allen Gähres.
The spring congress of the “Deutsche Physikalische Gesellschaft e.V.” (German Physical Society (incorporated society)) took place in Ulm in March. An Einstein opera was played in the “Grosses Haus” (Great House) of the Ulm Theatre from March to May. The cultural highlight of the Einstein year in Ulm, an Einstein exhibition, was presented in the town house on Muensterplatz from March 12 to August 29.
Illustrations Credits:
Ulmer Stadtarchiv – Vorlage Stadtarchiv Ulm, G2 Einstein: 1
Bibliography:
| Hrsg. Hans Eugen Specker | Forschungen zur Geschichte der Stadt Ulm, Band 1, Einstein und Ulm | Ulm 1979 |
| Editors: John Stachel, a. o. | The Collected Papers of Albert Einstein, Volume 1 | Princeton 1987 |

 DEUTSCH
DEUTSCH